|
|
GeoAstro Applets |
Astronomy |
Chaos Game |
Java |
Miscel- laneous |
Ancient Theories of the Sun:
3. Eccentric and Equant
Model Applet
1. Eccentric Model
Applet
2. Epicyclic Model
Applet
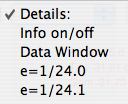 |
Select from
the Details menu. e is distance
between the center (+) and the Earth, which is
equal to the distance between the
center and the equant point, both measured in
units of the radius. For e=0 the
equant point and the Earth coincide with the
center. |
 |
Select the time interval. |
 |
Uncheck the box
to remove the equant point (setting it to the
center). |
Apogee
A
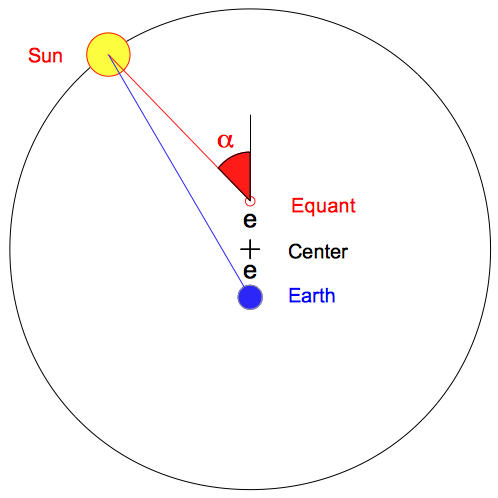
P
Perigee
| In addition to
the eccentric position of the Earth there is an equant point -
which is opposite to the Earth and sees the planet or
the Sun move at a uniform angular speed (angle α) on
the black circle (radius r) around the center (+). rMin=r-e, rMax=r+e eccentricity=(rMax-rMin)/(rMax+rMin)=e/r |
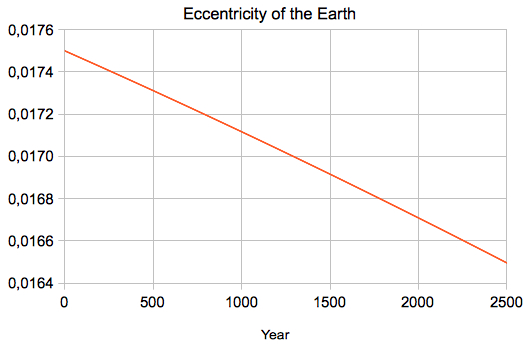
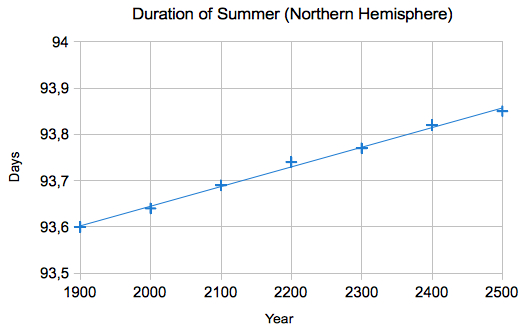
Diagram computed by e=1/60
The results are in very
good agreement with my Seasons Applet
The following
diagrams are showing the between the precise
heliocentric longitude (computed by my Planet
applet) and the value from the eccentric and
equant model: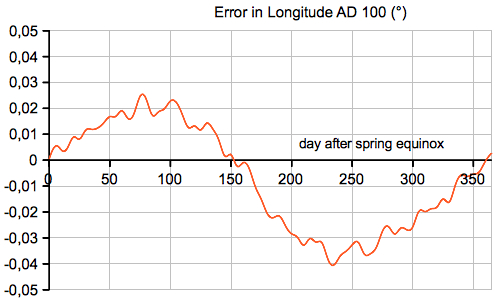 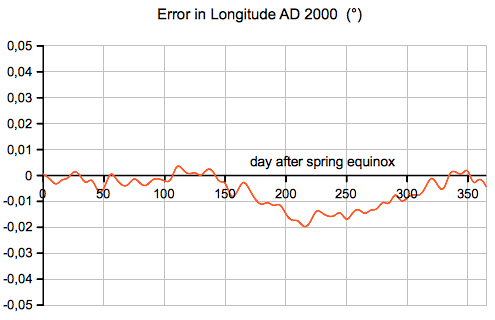 The following diagram is showing the between the precise distance of the Sun (computed by my Planet applet) and the value from the eccentric and equant model (e=1/60): 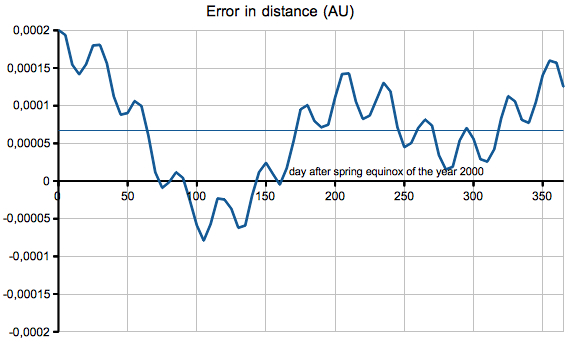 |
|
|
|
Hipparchus:
Orbit of the Sun (Wikipedia) Gemini Elementa Astronomiae, editit C. Manitius (PDF, Greek/German) Des Claudius Ptolemäus Handbuch
der Astronomie (Übers. Karl Manitius) |
| Books |
| James Evans: The History and Prctice of
Ancient Astronomy, Oxford University Press, 1998, Chapter Five: Solar Theory. Hugh Thurston: Early Astronomy, Springer, Berlin/New York 1994. Jean Meeus: Astronomical Tables of the Sun, Moon and Planets. 2nd ed., Willmann-Bell, Richmond 1995. |
Updated:
2023, Oct 07