|
|
GeoAstro Applets |
Astronomy |
Chaos Game |
Java |
Miscel- laneous |
Foster-Lambert
Sundial Applet
| The movable
gnomon is directed exactly halfway between the
celestial pole and the zenith, producing
a circular ring of equiangular hour points. This
feature was discovered and published in 1654 by
Samuel Foster, and rediscovered by Johann-Heinrich
Lambert in 1777. The position of the gnomon is indicated by a blue dot:  Check the box "Draw" of the applet to draw the construction of the dial:  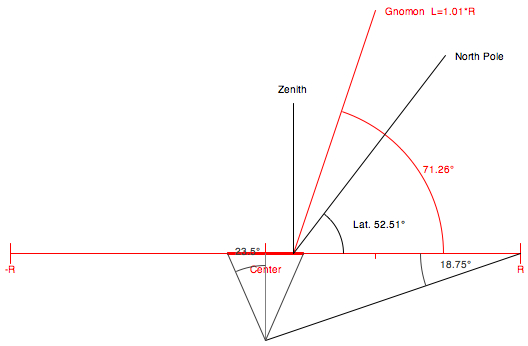 Latitude 52.51° N (Berlin) The angle
between the gnomon and the horizontal plane is
(latitude φ):
(90°+φ)/2
The
minimum length of the gnomon is (Radius R):
R*cos(φ-23.44°)/[cos(23.44°)*cos(0.5*(90°-φ))]
On the
north-south axis the displacement of the
gnomon from the center depends on the
declination δ and the latitude φ:
R*tan(0.5*(90°-φ))*tan(δ)
At
noon on the day of summer solstice (winter
solstice for the southern hemisphere) the
shadow of the top of the gnomon lies on
the radius (elevation angle 90°-φ+23.44):
 |
|
|
Enter latitude in decimal degrees and press return key, |
 |
Select "Solar
Time" or "Standard Time" from the menu. Chosing "Standard Time" the circle of the hour points will by rotated by an angle determined by the longitude and the current equation of time. |
  |
You may use the keys "y", "m", "d", "h",
"n" to increase
the year, month, date, hour, or minute, Click
the applet first !
|
My Sundial Applet Collection
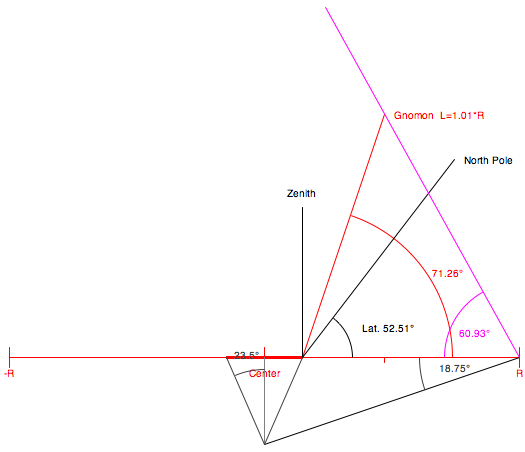
A second gnomon
(perpendicular to the first) may be added, checking the
box: 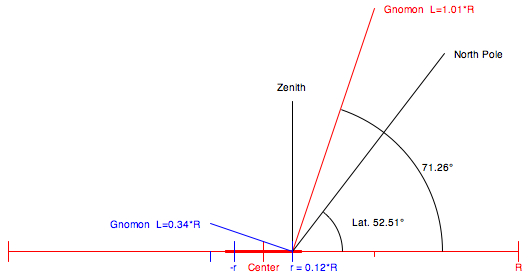 The double
gnomon mode is implemented for solar time only.
For high latitudes the corresponding inner circle of the hour points will be very small. φ = 30°: r
= 0.33*R
The double gnomon sundial is
self-aligning, rotating it until both scales
indicate the same time. φ = 40°: r = 0.22*R φ = 50°: r = 0.13*R φ = 55°: r = 0.10*R |
| Books |
| Denis Savoie: La
Gnomonique, Les Belles Lettres, Paris 2007; p
186-190. Jörg Meyer: Die Sonnenuhr und ihre Theorie, Harri Deutsch, Frankfurt 2008; p 338-342. R. Newton Mayall, Margret W: Mayall: Sundials - Their Construction and Use, Dover Publ., Mineola N.Y. 1994; p 190-192. Rene R. J. Rohr: Die Sonnenuhr - Geschichte Theorie Funktion, Callwey, München 1982; p 124-127. Rene R. J. Rohr: Sundials: History, Theory, and Practice, Dover Publ., Mineola N.Y. 1996. |
|
|
|
Foster-Lambert sundial (The Sundial Primer) Equatorial projection sundialsFoster-Lambert Sundial at Mutenz, Switzerland |
Updated:
2023, Oct 12
©
2010-2023 J. Giesen
![]()


