|
|
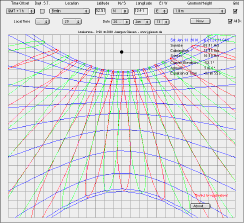 |
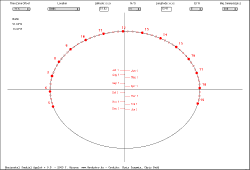
An analemma is the figure-of-eight shape that results if the Sun's position in the sky is recorded at the same time of day throughout the year. The gnomon of a sundial draws a similar figure. |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
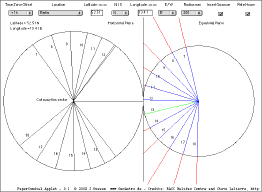 |
Make your own sundial just by folding a
sheet of paper. |
|
|
|||
| 4.
Cylinder Sundial |
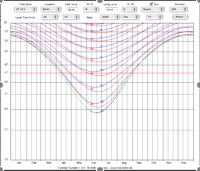 |
Java applet drawing a cylinder sundial indicating clock time. | |
| 5. Sundial Box |
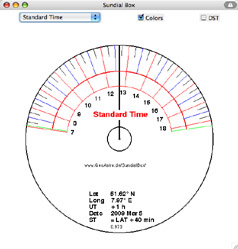 |
Java applet drawing an
hour scale for a Compact Disk. |
|
|
|||
| 6. Spider Sundial | 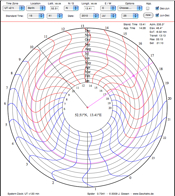 |
A horizontal sundial using a vertical gnomon. It depends on the azimuth angle of the Sun. | |
|
|||
| 7.
Spider: Vertical and Polar Pointing Gnomon |
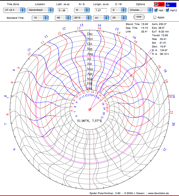 |
A horizontal sundial using a vertical gnomon. It depends on the azimuth angle of the Sun. | |
|
|||
| 8. North Finder | 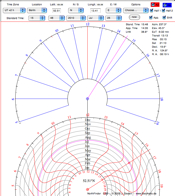 |
This horizontal sundial combines two different principles and is self-aligning to true north. | |
|
|||
| 9. Bifilar Sundial | 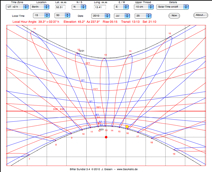 |
This sundial
uses two non-intersecting threads parallel to the
horizontal dial plane. The upper thread (distance a
above the plane) is oriented North-South, the lower
(distance b) is orthogonal to the first. The
intersection of the two threads' shadows gives the
time. |
|
|
|||
| 10. Cone Sundial | 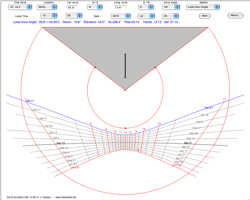 |
This sundial
uses a horizontal gnomon. The hour lines and the date
lines are drawn on to a cone. |
|
|
|||
| 11. Babylonian, Italian, Unequal Hours Sundial | 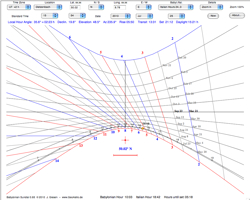 |
The Babylonian
system divides the day into 24 equally long hours
beginning at sunrise and ending with the following
sunrise. Italian hours begin counting at sunset and ends 24 hours later with the following sunset. |
|
|
|||
| 12. Pingre Sundial | 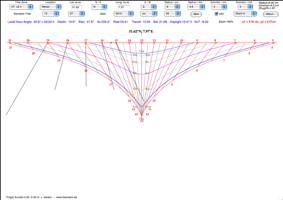 |
This unique
sundial was invented and designed by the French
astronomer Alexandre Guy Pingré (1711 - 1796). It is similar to the cylinder sundial, but there are multiple gnomons in a horizontal plane, perpendicular to the cylinder. |
|
|
|||
| 13. Daylight Hours Sundial | 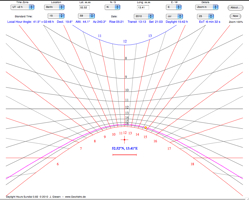 |
The gnomon of
this sundial is vertical. The shadow of it's top on
the horizontal plane is used to read the sundial. The declination lines are computed for full numbers of daylight hours which depend on the latitude of the observer and the declination of the Sun. |
|
|
|||
| 14. Sidereal Time Sundial | 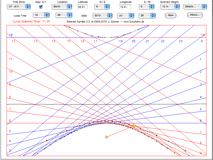 |
This horizontal sundial is showing the local sidereal time, which is defined as the hour angle of the vernal equinox. | |
|
|||
| 15. Foster-Lambert Sundial |  |
The gnomon produces a circular ring of equiangular hour points. | |
|
|||
| 16.
Azimuthal Orthographic Sundial |
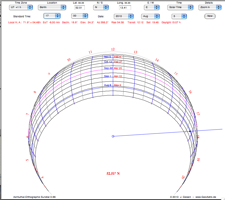 |
Azimuthal Sundial for both
solar and standard time. |
|
|
|||
| 17. Gnomon | 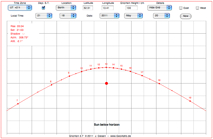 |
This type of
sundial has a vertical gnomon casting the shadow on a horizontal plane. |
|
Additional Applets: |
|||
| Sun: Declination, Equation of Time, Transit Time |
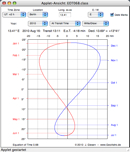 |
Tables, and diagrams. |
|
|
|
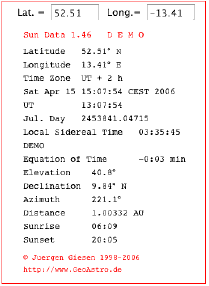 |
The applets computes the times of sunrise and sunset, and more astronomical data, which are updated every second. |
|
|
|
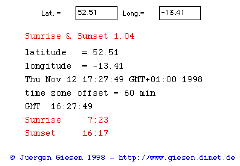 |
The applet displays the times of sunrise and sunset. |
|
|
Equation of Time |
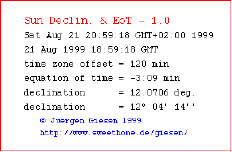 |
The applet displays the current declination of the sun and the equation of time. |
|
|
& Equation of Time |
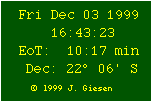 |
The applet displays the current declination of the sun and the equation of time. |
|
|
|
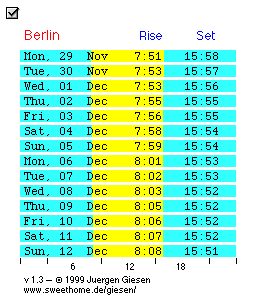 |
You may edit the applet parameters for your location and the number of lines. |
|
|
|
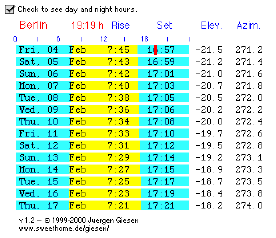 |
You may edit the applet parameters for your location and the number of lines. |
|
|
|||
| SunClock | 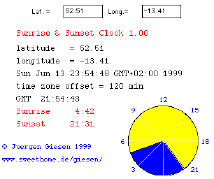 |
||
|
|||
| Twilight Clock | 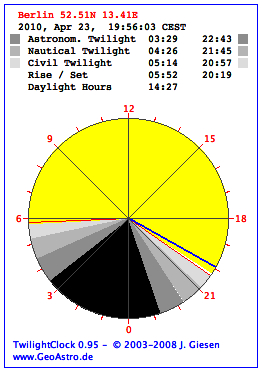 |
||
| Spider Sundial |
 |
||
|
On my Home Page: Astronomie by JavaScript Home Page: http://www.jgiesen.de Last Modified: 2012, May 12 |
|||
